Does dermatitis refer to the same condition as eczema and are contact dermatitis and contact eczema the same thing? Yes, eczema and dermatitis are interchangeable terms used by dermatologists. It’s usual, when referring to a contact dermatitis to call it a dermatitis rather than an eczema, but they are the same thing.
Are there different types of contact dermatitis? What’s the difference between irritants and allergens?
There is allergic contact dermatitis, which is mediated through an immune mechanism, this means that the person is specifically allergic to what they have come in to contact with their skin. Their body has had to go through a process whereby they have become allergic to this substance and have T lymphocytes that specifically targeted against the allergen. Then, when they’re faced with the allergen, their immune system recognizes it and amplifies up an immune response.
Whereas, in relation to an irritant, the person has no specific allergy to it and therefore there are no specifically sensitized T lymphocytes, instead, the irritant works through a toxic mechanism. The chemical is toxic to the skin or to the immune system and it excites an immune response, through a toxic mechanism rather than through an allergic one. The results of a dermatitis or eczema can be almost identical and so a dermatologist cannot determine whether the contact dermatitis has been caused by an irritant or allergen by looking at it.
However, the distribution of the dermatitis may indicate which of the two, allergic or irritant, it may be. Additionally, allergic and irritant types of dermatitis are not mutually exclusive and you can have a dermatitis which is a mixture of both types. An irritant dermatitis can predispose you to the development of an allergic dermatitis, because it up-regulates the immune system. In addition to irritant and allergic contact dermatitis, endogenous factors, for example a background of atopic eczema, may make it more likely for you to develop an irritant dermatitis and even more likely to develop certain types of allergic contact dermatitis as well.
How are the different types of dermatitis diagnosed?
Firstly, a dermatologist can get an idea of the possible type of dermatitis present by looking at its distribution of the rash and whether it has spread across the: face, hands, feet or the body etc. This can give an indication of the underlying cause. For example, facial dermatitis in a woman might suggest the cause to be a cosmetic or if it’s a hand dermatitis in a man, you might want to know what job they have. Whether they’re involved in industrial processes where they might be exposed to certain chemicals or they might in fact be allergic to personal protective gear. Another explanation could be that they’re allergic to something they’ve been applying to their skin.
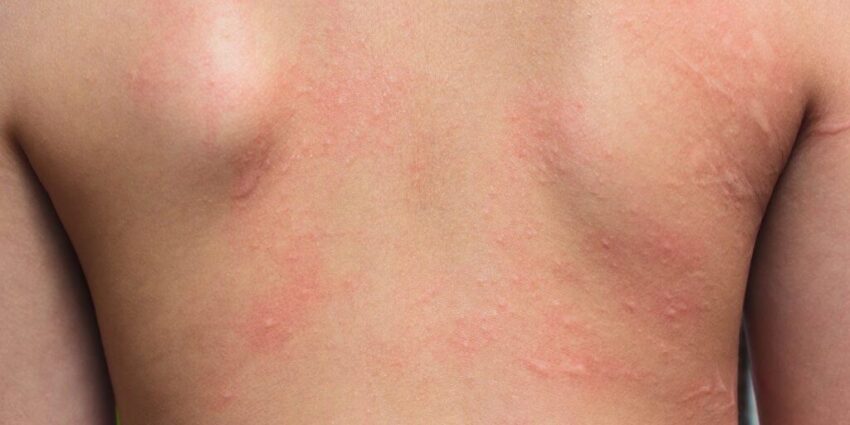
The history, and how the dermatitis started, is also key to understanding what may be causing the episode, for example whether it shows periodically with periods of no symptoms or maybe it went away when the patient went on holiday, this sort of information can give you an idea of the origin and what may be the cause. There is also a patch test that can be carried out by a dermatologist, this is the best investigation for contact dermatitis. Patch testing tests for a delayed type allergy (hypersensitivity) which is a T-cell mediated response. Patch testing is carried out by placing small amounts of a wide variety of chemicals on people’s backs using special chambers on tape.
Dermatologists use a set of known, standard substances and concentrations which come in a kit that have been specially prepared for this purpose. It’s important that the test is carried out in a controlled manner. In patch testing, these materials are placed on the back for two days and then removed and marked, this is when the back is read for the first time. Typically, between 40 and 100 different individual materials are tested at each time. The results are read on day two and on day four following application of the different substances. If there’s a reaction, you get a small red, itchy, raised area of eczema. Sometimes small little bumps called papules or even small blisters can be present. Blistering indicates a more severe type of reaction.
A reaction to different chemicals on the patch test can help you identify the substance the person may have been exposed to and is causing their eczema. The next stage is to use the information from the patch test and translate the reaction into the clinical context. For example, if somebody has had a delayed allergic reaction to nickel, which is the most common substance that people react to. However, this doesn’t necessarily mean that their rash is due to nickel, if a patient has had a reaction to a number of chemicals in the patch test, all different possibilities must be taken into account in order to find the most likely cause to the patient’s eczema.
What are the main symptoms of contact dermatitis?
When people generally present with an eczema, there is redness, scaling and itching. Itchiness is the main symptom, but sometimes blistering can occur too. Contact dermatitis can be acute or chronic. In acute contact dermatitis, somebody is exposed to something and then within two or three days or even less, they develop these symptoms. This type of dermatitis is often on the face or hands, but can occur anywhere. With chronic contact dermatitis, you may have been an acute episode, but subsequently a chronic eczema has developed.
In chronic eczema, the skin becomes thickened and scaly with cracks. It’s not often red, inflamed or blistering like in an acute episode, it has already been through that stage and has thickened up. Chronic dermatitis will have been in existence for several weeks, but both acute and chronic conditions may be caused by either a contact allergy or irritancy.
Who does contact dermatitis typically affect and are there any risk factors that make people more likely to develop contact dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis can affect anybody, however it is associated with certain occupations and we always looking for occupational causes. One common group of occupations where people might get contact dermatitis is healthcare workers, because they’re exposed to a variety of things, and particularly common is a reaction to their personal protective equipment such as gloves and an irritancy or allergy from hand washing substances. However, a reaction to the latex in gloves etc. is not an example of a contact dermatitis but is caused by contact urticaria, which evokes an immunoglobulin E mediated response rather than a T cell mediated one.
People in industrial jobs like building trades can be allergic to: chromate, cement or rubber chemicals, which can again be present in their protective clothing. Cement is commonly an irritant, but you can get both irritant and allergic reactions to it. Another group of people that may be susceptible to developing contact dermatitis are cleaners and people who handle similar chemicals on a regular basis. Other common industries are in food preparation where people often have an irritant dermatitis rather than allergic one. Although, you can be allergic to a whole variety of different foods this is another example of a contact urticaria allergy.
If you have other allergies are you more likely to get contact dermatitis, for example if you have food allergies?
It is common for someone who has food allergies to also have atopic eczema. However having food allergies doesn’t necessarily make it more likely for a p